Windows
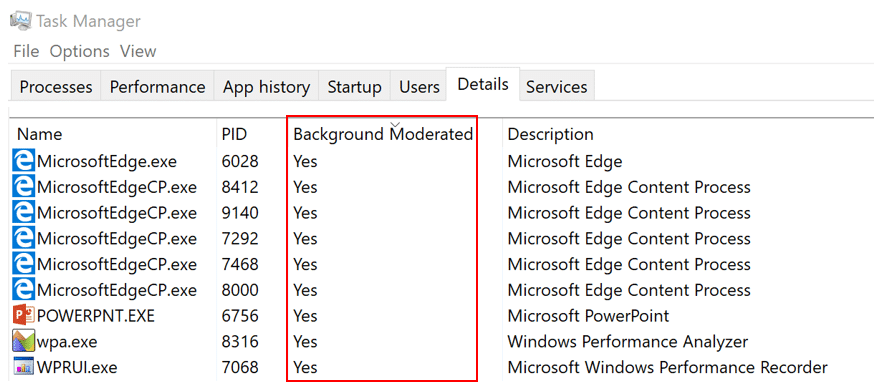
The task manager shows which processes are in the “background moderated” mode to conserve battery power. Source: Microsoft
In January 2017, with the build of Insider Preview 15002, Microsoft began an experiment with a partial suppression of the activity of background applications. Based on the results of the experiment on a limited number of devices, it became clear that the Power Throttling feature saves up to 11% of the battery charge in the most extreme cases. Therefore, now it is decided to make this function part of the build 16176 in the Insider Preview. This build was released a few days ago, it was the first update after the Creators Update.
In Power Throttling mode background processes are executed in the most energy-saving mode. The process goes on, but with minimal energy. Microsoft says that since January it has made improvements in Power Throttling, listening to the wishes of users, so this function should help save energy on many computers.
The Power Throttling function uses the hardware capabilities of modern processors, namely technology Speed Shift. While the function is supported only on Intel Core processors of the 6th generation and later. This is Skylake and Kaby Lake. Microsoft is now working to extend support to other processors, it can happen in the next few months.
In practice, energy conservation in background processes requires the introduction of a “complex detection system” at the operating system level, Microsoft explains in the official blog. Windows needs to determine which of the background applications are important to the user, and which ones are not important. For example, important background applications include music playback, as well as some other important tasks. For most applications, “smart detection” works well, but on some applications it may be buggy. Microsoft calls to report situations when Power Throttling did not work correctly. To do this, run the Feedback Hub feedback tool and report the problem in the category Power and Battery → Throttled Applications.
In addition, you can independently control the aggressiveness of suppressing background applications via the slider.

There, this mode can be made more aggressive compared to the recommended value (Battery Saver) or disable altogether (Best Perfomance).
In the end, it is possible to exclude specific applications from the mode of “background moderation “. This is done through the battery properties (Settings → System → Battery). In the “Battery Usage by App” window, the desired application is selected and the “Managed by Windows” setting is set to “Off.”
When the notebook is powered from the network, the Power Throttling function is not activated. In this regard, Microsoft recommends running benchmarks, for example, only in the network mode to obtain an objective result of performance measurements.
Microsoft promises to make changes to the API so that individual applications have direct access to power saving settings while running In the background.

That’s what the Task Manager looked like in the Insider Preview (build 15002)
Note . In the final Power Throttling function, a change has been made to the task manager: for the background applications, instead of the term “Muted” (Throttled), the phrase “Moderated in the background” (Background Moderated) is used.
Interestingly, the Power Throttling function in Windows 10 Something similar to the battery-saving functions in modern browsers. There it is also done by “muffling” the background tabs – scripts, flash, etc. For example, the Chrome browser from the penultimate version of Chrome 57 actively suppresses the background tabs. There it is done purely on a program level. Each WebView component has a budget (in seconds) for running the timers in the background. The timer can not start if the budget is negative. After the timer is executed, its operating time is subtracted from the budget. The budget automatically replenishes with time (0.01 from the budget with every second of real time).

Suppressing the activity of background tabs in Chrome 57
The main reason for implementing this function is that some badly designed applications (for example, analytics scripts and javascript advertising) consume a lot of CPU resources, although they are in the background. This negatively affects the performance of the browser and consumes battery power on mobile devices.
At the software level, the function of suppressing background applications App Nap in macOS. In macOS this way, you can even increase the performance of the active application.









