scientific
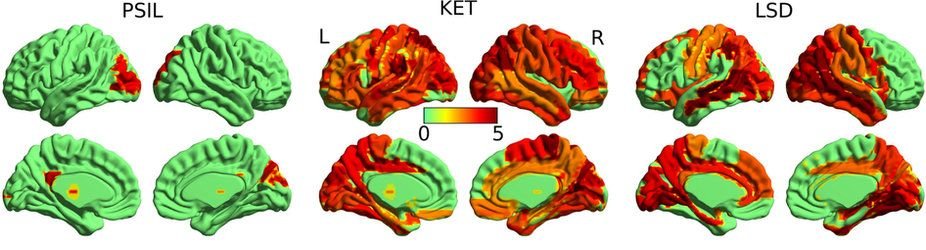
Averaged changes in the level of complexity of brain activity using the Lempel-Ziv algorithm by one channel (this is only one of several measured mathematical metrics Complexity of signals) for three psychotropic drugs: psilocybin, ketamine and LSD. Red color corresponds to an increase in the level of difficulty. Image: University of Sussex
Understanding the neurological basis of consciousness is one of the most difficult puzzles that confronts modern science. The wording of “consciousness” therefore varies from extremely broad to extremely narrow, but at an intuitive level everyone roughly understands that there is a difference between the level of consciousness (to what extent is a person conscious) and the content of consciousness (thoughts, sensations, feelings). Accordingly, most neurological studies study these two measurements separately. By brain activity, it is much easier to establish the difference between levels of consciousness – brain activity in an unconscious person and in a person in consciousness is well marked. Formally, this is expressed through the index of the diversity of neural signals – the mathematical characteristic of the level of consciousness.
It would seem that the difference between the levels is clearly established and documented. But in the results of magnetic-encephalography, scientists from the Sackler Center for Consciousness Studies at the University of Sussex (Great Britain) discovered very strong and sustained bursts of a variety of neuronal signals in the brains of patients after taking psychoactive doses of some drugs: ketamine, LSD, and psilocybin. The complexity of brain activity during these outbursts in humans is much higher than at the normal level of consciousness. Scientific work was published on April 19, 2017 in the journal Scientific Reports (doi: 10.1038 / srep46421).
Amplified brain activity under the influence of psychotropic drugs scientists were registered earlier, although in most countries such experiments are difficult Due to legislative restrictions on the use of psychotropic drugs. But in the UK, scientists managed to obtain permission. A year ago, a group from Imperial College London published the first detailed brain scans, which is under the influence of LSD. It was found out that in this condition the visual cortex’s connection with other areas is significantly increased. In other words, after taking LSD, the processing of visual information in the brain is no longer limited to the visual cortex. All areas of the brain begin to participate in the formation of visual images in patients. This is especially interesting considering that during the experiment, the eyes were closed in patients. In fact, patients began to “see with their eyes closed.”
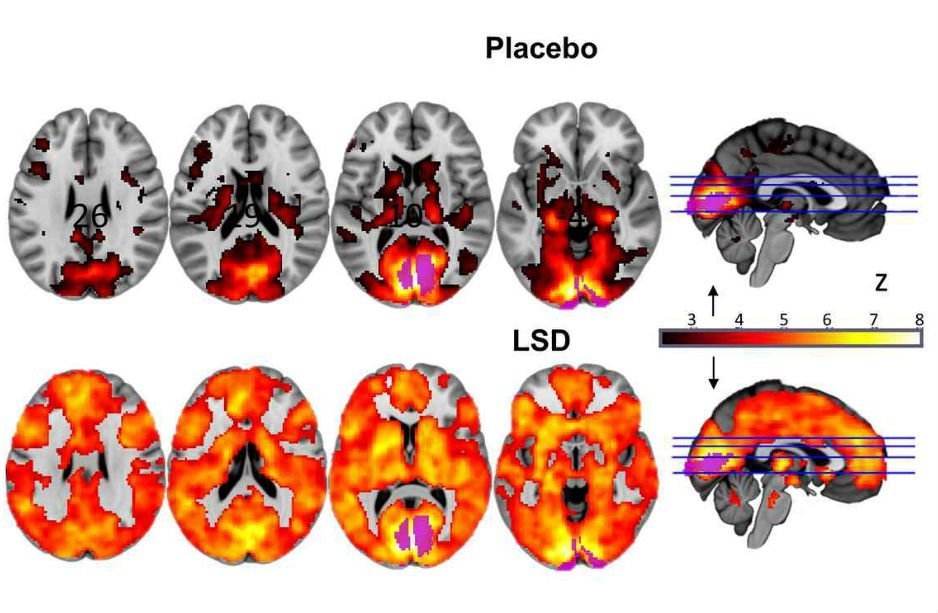
In the current experience, scientists went further – and concentrated on quantifying the level of consciousness, that is, the mathematical index of the diversity of neuronal signals . For the analysis, we took the data of three previous experiments, including those published a year ago by colleagues from the Imperial College of London. As expected, in the overactive state, the brain exhibits unusually complex activity, which is much higher than activity in the “ordinary” conscious state. The difference between these two indicators is about the same as the difference in consciousness between a waking and sleeping person. This gives grounds to talk about the third, higher level of consciousness, which is above wakefulness as much as wakefulness is above sleep. On the site Neuroscience News dedicated to the news of neurology, this discovery was called “the first evidence of a higher state of consciousness.” However, with the proviso that only in this particular mathematical metric.
The authors of the scientific work say that additional experiments are required to confirm these results, but they express “restrained admiration” for what they saw on the results of the magnetic-encephalography: “In psychedelic The electrical activity of the brain is less predictable and less “integrated” than in the normal conscious state of wakefulness, as measured by the overall diversity of neuronal signals. – says Professor Anil Seth (Anil Seth), co-author of the scientific work. “Since this metric has already shown its value as an indicator of the” level of consciousness, “we can talk about the psychedelic state of consciousness as a higher” level of consciousness “than the normal level, but only with respect to this particular mathematical metric.”
It is also interesting that in the activity of the brain from all three drugs there are similar changes, but with varying degrees of intensity.
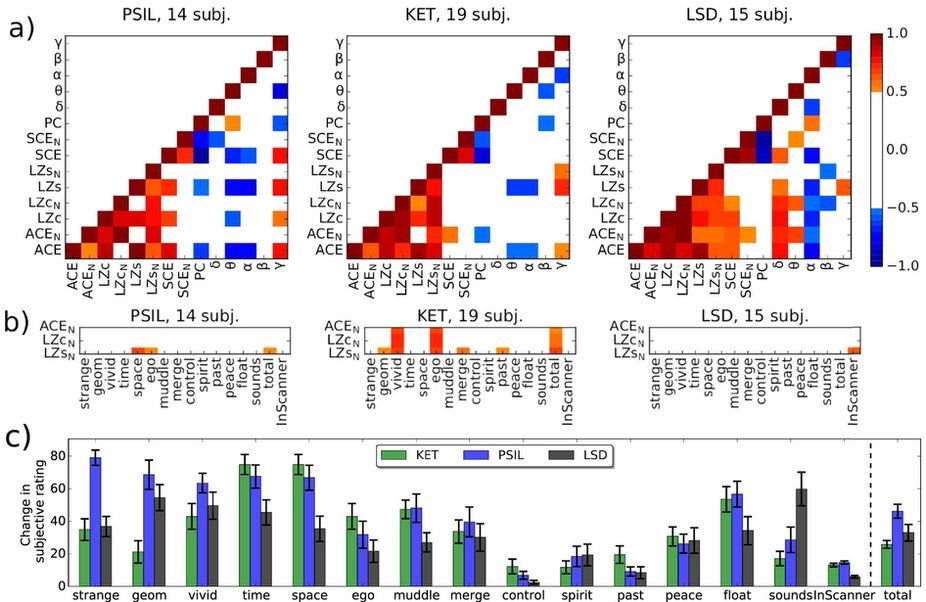
The figure in the upper row reflects the magnitude of the Pearson correlation coefficients for patients The They took drugs, compared to patients who took placebo, according to different metrics. In the lower row, there is an average difference in answers to questions on different topics.
Scientists emphasize that the results of measurements do not give grounds for believing that a more active state of consciousness is “better” or “preferable” than the usual state. But these data make it possible to understand what is happening in the brain of a patient under the influence of psychotropic drugs. Scientists hope that the results of the study will be an argument for the authorities to allow the testing of these powerful substances for the treatment of clinical depression under strict medical supervision. They believe that only under supervision one can predict the positive effect of such treatment.