Geektimes
Along with the development of mechanical systems of the car, engineers were constantly striving to add something to the electronic stuffing, to make the car safer, more manageable and smarter. Today, for this, there are all prerequisites: the IT history is developing at a tremendous pace, automakers are ready to cooperate and carry out advanced developments, corporations invest in the development of vehicles. Geektimes Meanwhile, the “mind” of cars developed steadily, for more than half a century. All this time he took various forms and went into different concepts: from security to entertainment. history The modern phase of evolution has gone so far that it is already incomprehensible, the software defines iron or hardware – software. So, it’s time to write about cars on Geektimes.
Let’s remember how it all began
The first technological revolution in the automotive industry was the interest of automobile companies in electric starters – they were first installed in 1911. Then innovations began to concern the driver’s convenience and even his entertainment behind the wheel: in 1925 a cigarette lighter appeared, in 1930 – radio, in 1956 – power steering, in 1970 – a cassette deck, in 1984 – airbags. A year later – CD players, in 1994 – a panel of devices for computer diagnostics of the car, in 1995 – geektimes GPS, in 2000 – USB and Bluetooth, the first swallows “connected” to the whole car.
The first experience of creating a smart car occurred in the middle XX century. General Motors Firebird II – four-seater car in 1956 with independent suspension. Under the titanium hull was a gas turbine engine Whirlfire GT-304 for 200 hp, an electrical package and an integrated air conditioning system of a level no worse than at the beginning of the XXI century. Firebird II in terms of design and ergonomics continued the version of the 1953 car, which was called the “jet aircraft on wheels” (the developers and engineers were really inspired by the concepts of fighters of that time). However, in Firebird II, for the first time, a structure was used to travel on the highway of the future – a complex control system that was supposed to interact with an electric wire built into the roadway to send signals and serve as a guide for the newest cars. It was assumed that the electromagnetic field minimizes dangerous situations on the road, reducing the human factor. At that time it was too bold a model that made a furor at exhibitions, but never got into mass production.

The future roads were built in Europe and the USA. The first production car, which really began to interact with them, was Citroen DS – the legendary light car, which took the third place in the rating of cars of the century. Low-power engine 75 hp Nothing stood out in those days, but the car was distinguished by an advanced transmission, combined with the steering, brakes and hydropneumatic suspension. This design has outstripped the development of the automotive industry for many years to come. Citroen DS was able to interact with the highway with the help of an electric signal, but there was no question of any independent autopilot – it was more fun. By the way, it was incredible popularity, advanced technology and even a relatively illusory, but autopilot made this Citroen a flying Fantomas car.

Experiments with on-board computers in the 60-70s. Were conducted, but did not enter the series. It is worth remembering the experimental Chrysler Plymouth, which was equipped with an on-board computer (well, as far as you can call an on-board computer that occupied half of the rear seat) and a generator for powering the system, put on the roof of the car. Laboratory tests were conducted for 10 years, but there was no question of serial production.
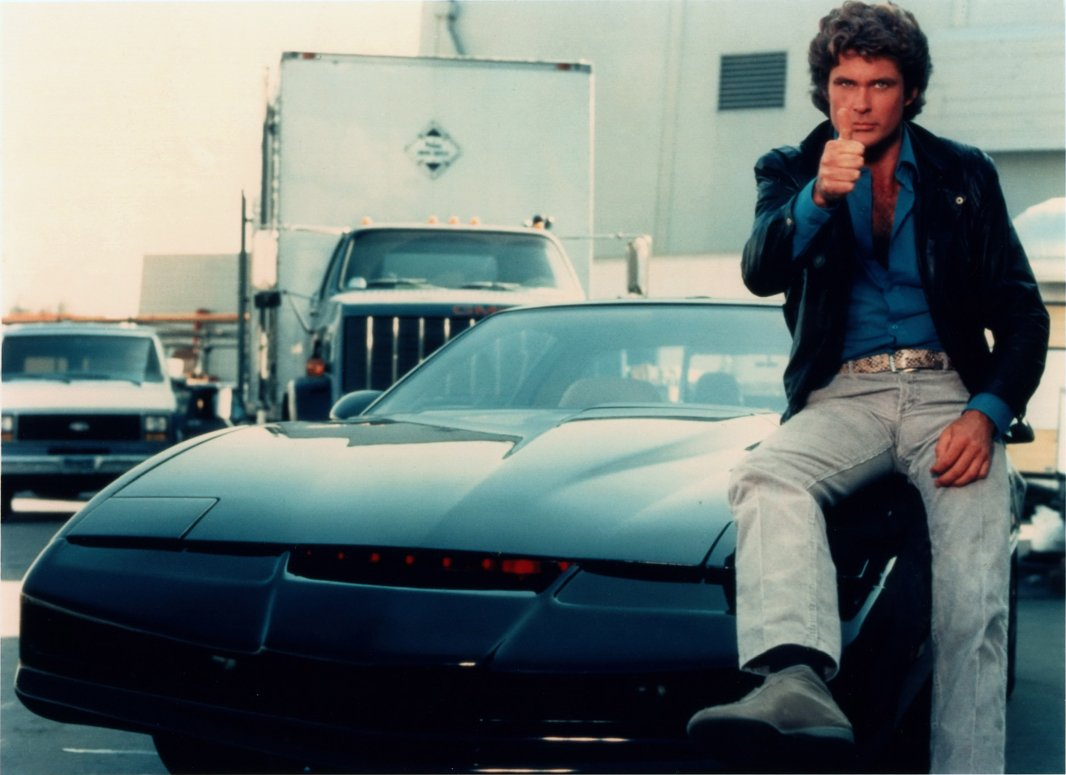
Nevertheless, neither the engineering thought nor the imagination of the Futurists did not stop for a minute – humanity sought in cars not only for luxury or a means of transportation, but also for an intelligent helper capable of facilitating life, making roads safer, working for a person . This desire was reflected in the movies – after several films with “talking” machines, these hits became a series of films about James Bond with his heaped cars and, of course, the legendary “Knight of the Roads.” Clever, humorous KITT car based on the Pontiac Firebird Trans AM not only developed speed at 500 km / h and was almost invulnerable, but also was able to talk, ride on full autopilot and control all electronic devices at a distance.
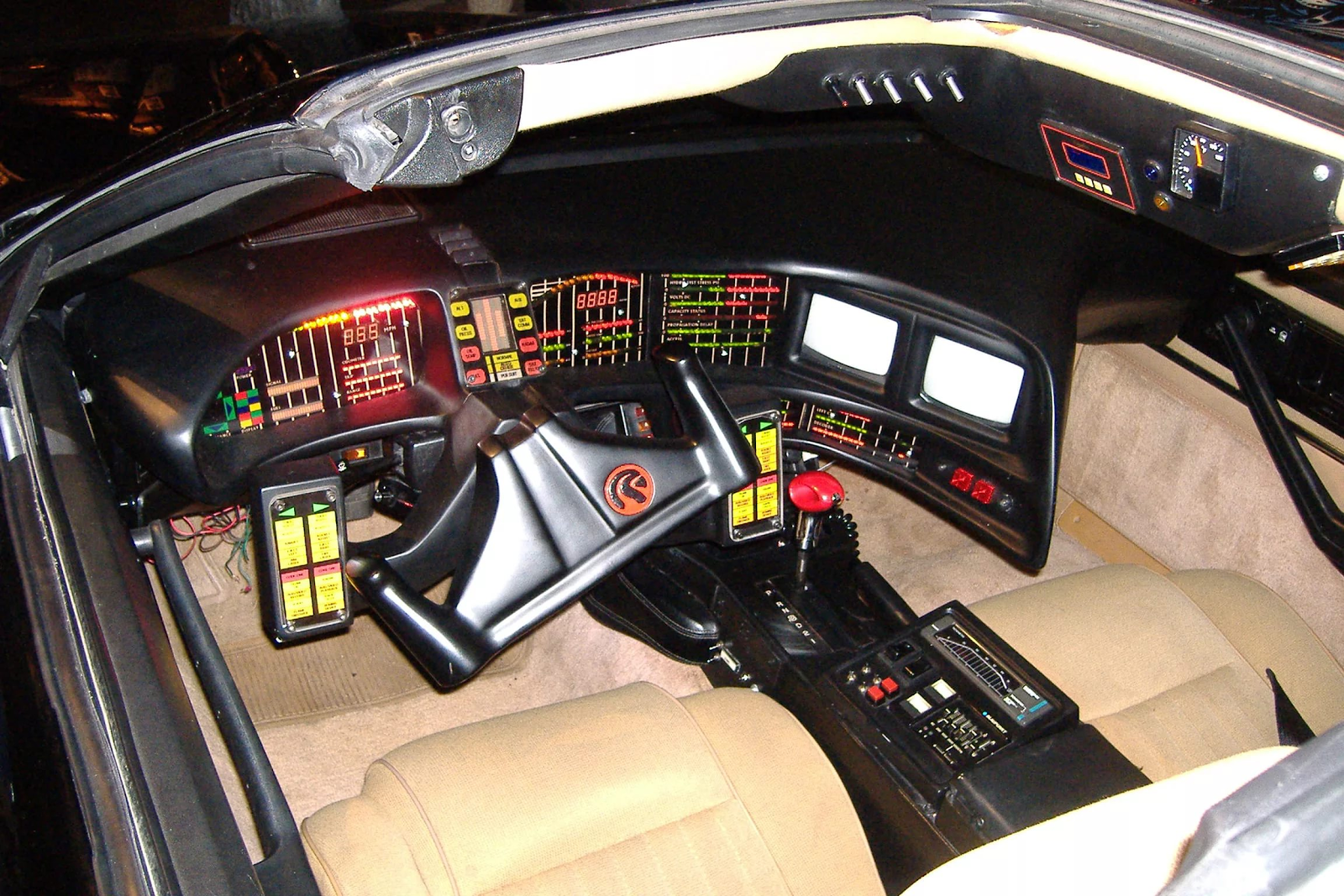

KITT inside
Probably utilitarian reality did not coincide with the dreams of the engineers of the past – the shaping of the appearance of modern smart cars was influenced by commerce and notorious business expediency.
- Automakers began to strive to meet the demands of a mass consumer who is spoiled by the IT industry. The mind of cars was cruise control, media devices for playing content, built-in phones in the 80-90’s and so on.
- Tablet and smartphone manufacturers began lobbying their interests to integrate into cars (for example, some Samsung cars incorporate Samsung tablets).
- Users began to show increased requirements for electronic filling: from entertainment content to security systems and the ability to work with alerts on the state of the car.
Modern smart cars
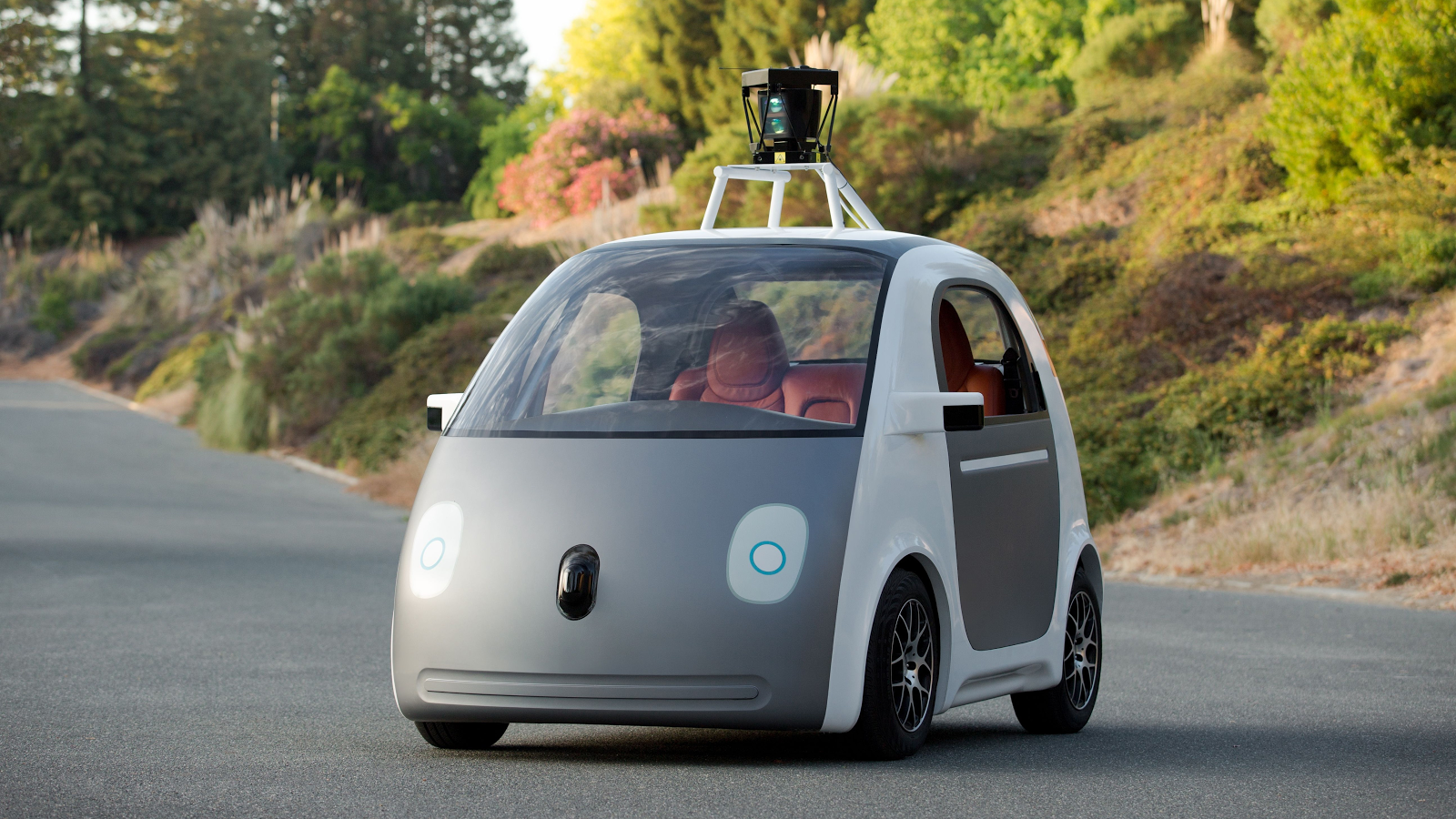
One of the first prototypes was proposed by Google – Google Car. This mini-car with an unprecedented level of autonomy. The car is designed for two people, has two engines, non-standard body materials, fully electric, speeds up to 25 mph (slightly more than 40 km / h), controlled from the start button and does not require the presence of a person except as a passenger. Naturally, it is integrated with Google services – in the central console you can watch videos and movies on Youtube, work with mail, fake in Chrome. By the way, the car is also built by Google, as the previous partners Lexux and Toyota expectedly imposed many restrictions on risky experiments. Entering the mass market of personal vehicles is extremely difficult, and in December 2016 Google (more precisely, holding Alphabet) curtailed the project to create its own unmanned vehicle. The company continues to develop autopilots, but already for ordinary automakers.

Car operating systems
Surely the majority of readers will first come to mind with Android OS. Indeed, this operating system is present in cars, and not only on embedded tablets. The distribution of the system began with the creation of an alliance Open Automotive Alliance, which included actually Google, NVIDIA, Audi, General Motors GM, Honda and Hyundai. We should not forget about Tesla, on board which are large 17-inch displays based on Android. However, for now, the use of this operating system is aimed primarily at creating information and entertainment car stuffing, including navigation functions.
iOS does not lag behind the competitor and, as long as the whole world waits by 2020 for the first i-mobile or i-Car (they say it will be that The unmanned vehicle based on the BMW i3), Apple implemented the Apple Carplay system, which allows you to connect the car control system from the iPhone from the 5th and up. Not all cars support the system, but most of the top manufacturers are already on the list. Of course, and here about the operating system is not talking – just the integration of devices on iOS in the infrastructure of the on-board computer. Again, the entertaining aspect comes to the forefront – here, and conversations are hands-free, and voice control of iTunes. By the way, Apple’s development of a UAV is strictly classified – try to find something besides general phrases about the Project Titan project.
Microsoft did not make a revolution, but chose a different vector of development and aimed at voice control of the car’s functions so as not to Distract the driver from the road. What happens with Microsoft’s software for cars can be described as a fully integrated smartphone in the car. Well, that is, you can wait for jokes from the category “wait, I’ll phone the phone.”
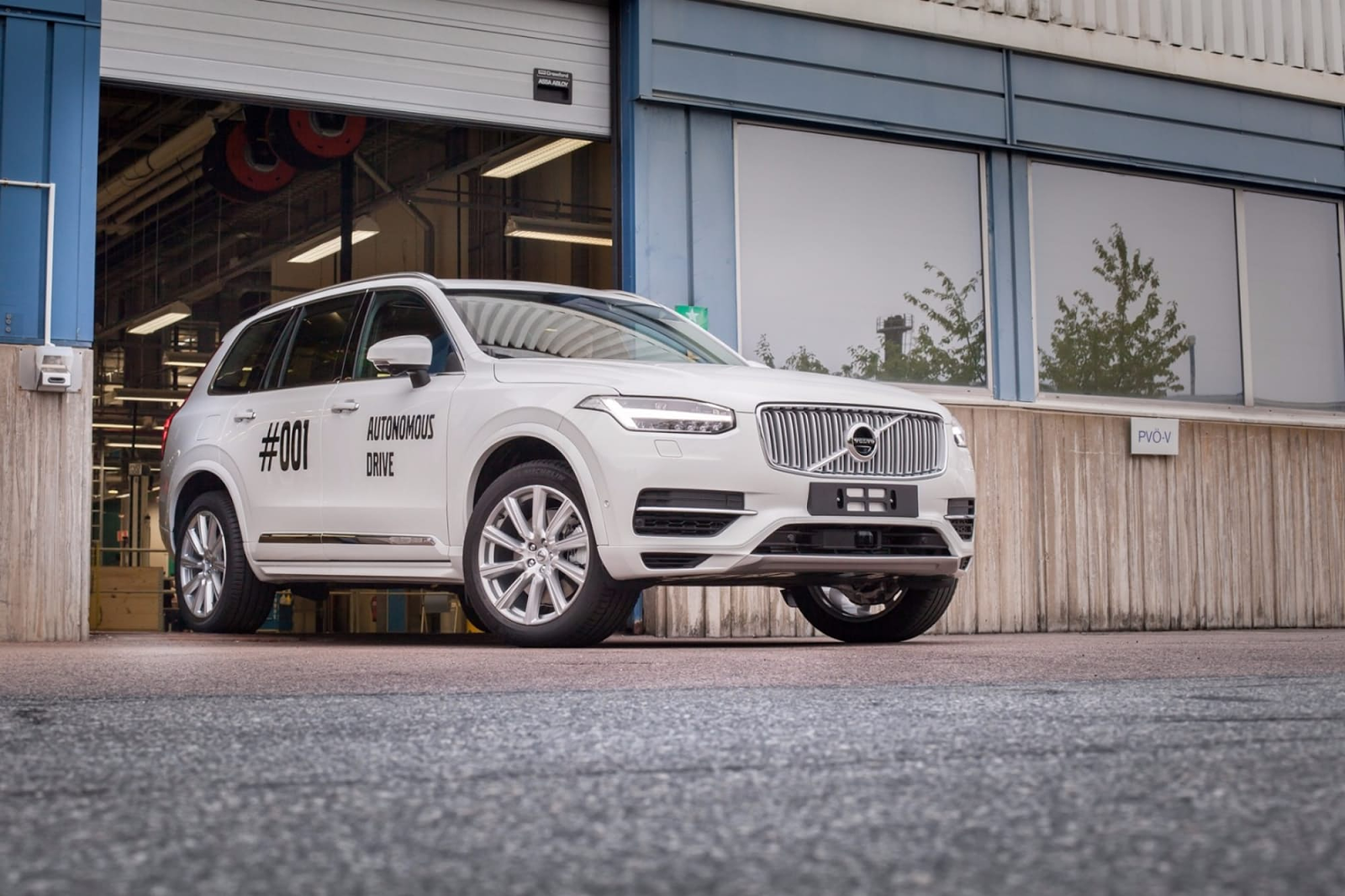
Already this year will test the autonomous driving system Drive Me from Volvo. Again, the assignment of the autonomy is for the convenience of the driver and traffic safety in the event that the owner of the car wants, for example, to have lunch at the wheel or dial a couple of messages in the messenger. Monitoring the environment, including the movement of pedestrians, will be possible with a clever combination of radar, cameras and lasers. Volvo focuses on the fact that they make real systems for real roads and consumers.
Volvo plans to attract tests to the most ordinary people of different sexes, ages, with different driving experience. During the testing, the company plans to collect “terabytes of data” about safety, usability, consumer experience, traffic flows, energy efficiency. Based on these data, the system will be further developed. The base car for testing is the XC90s.

In 2015, at the Geneva Motor Show, Italian studio Italdesign Giugiaro presented a GEA car (there is a version that it was partly a prototype of Audi A9, someone Refers to the near future of Audi) with completely autonomous control. Due to the fact that the driver behind the wheel (steering wheel-joystick) has nothing to do, the GEA provides three modes: a study, a gym and a rest room. In the Business mode, the salon provides two 19-inch monitors and a seat swivel for easy conversation. Wellness mode gives instructions for doing exercises on the handles built into the back seat. Finally, the Dream mode provides the driver with an extensive bed for sleeping. For all work options, the atmosphere and lighting are selected. The car can be controlled from the smartphone through a special application. The technical characteristics of the concept are also outstanding: 4 engines with a total power of 775 hp, a length of 5370 mm, a top speed of 250 km / h.
The features of Audi are clearly read
You can not leave a review of smart cars without attention to the legendary and, perhaps, the most German brand – BMW. The Bavarian automaker rarely looks back at others and goes to the rearguard of the market due to design and technology. According to the report of KPMG, the concern is leading in smart and unmanned vehicles.
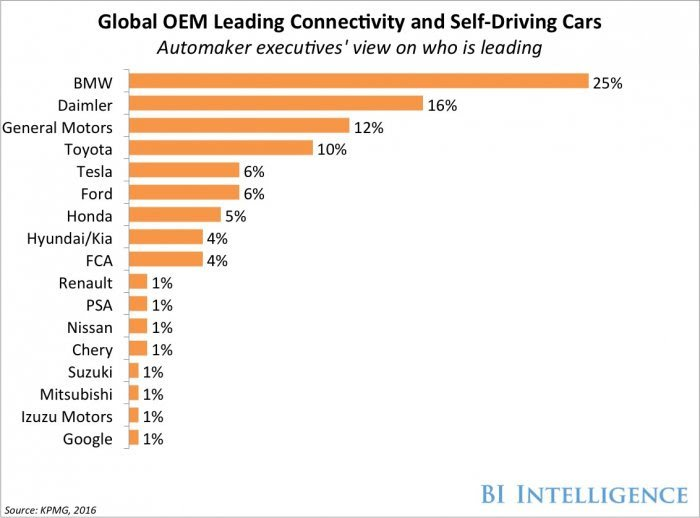
In the case of smart cars, the story is this: in addition to unmanned versions, which we will mention just below, there are serial cars, Who use everything that was created for smartkars of our time. At the beginning of 2017, the leaders include BMW i8, hybrid BMW X5 PHEV and BMW 7 (which, among other things, projects the data of the instrument panel on the windshield, has a heavily updated iDrive and perceives sensor control by gestures). These models of BMW (like others) are equipped with a large number of sensors and are smart from the point of view of safety – they analyze the situation on the road and, having a huge amount of information in their memory, literally predict unfavorable events, thereby preventing them. Vodafon’s SIM card is also integrated in the BMW, which operates in the roaming of almost any cellular operator in the world (in Russia everyone) and sends important information: to the driver – about the need for another maintenance, battery charge level, the nearest car-care centers, assistance points and even Hotels, restaurants, etc., and from the driver – about critical situations on the road. So, you can call up the help with one SOS button and the operator will get owner data and exact coordinates of the incident. If you can not reach the button – the car itself will give a distress signal to special services.
X5 with hybrid engine
Together with Mobileye and Intel, BMW is developing an iNEXT unmanned network software platform that will be designed as For installation on the cars of the concern, and for sale to other automakers. In 2021, BMW plans to release a third-level robotic car, which will still require the presence of a person (fourth level – it is possible to do anything except driving, the fifth level – the car itself will go where you need it).
It is simply impossible to tear the wheels off the wheels
Automobile software
AUTOSAR AUTomotive Open System ARchitecture) – an organization that aims to create a standardized open structure of software for the electronics of the car, in addition to infotainment systems. Such software should be scalable (distributed on different vehicles and platforms), localized, meeting the requirements for safety and maintainable throughout the life of the car. The standard AUTOSAR applies to the electronics of the body, power unit, chassis and safety system, as well as to multimedia systems, telematics and the interface between the driver and the car.
FlexRay standard onboard electronics protocol – high-speed network protocol for cars developed by the world consortium FlexRay, the founder of which is NXP together with BMW, DaimlerChrysler, Bosch, GM and Volkswagen. The data transfer rate reaches 10 Mbit / s. It is dozens of times faster than the modern CAN (Controller-Area Network) bus, and even more so – an obsolete and quite slow diagnostic OBD (On Board Diagnostic). FlexRay controllers will work for the control of those parts of the car in which the issue of modern diagnostics is equal to the issue of life and death: engine, transmission, suspension, brakes, steering.
Automotive Safety Restraints Bus specification (ASRB 2.0) – the standard of electronic vehicle systems, which are responsible for the physical safety of the driver and passengers, in particular.
Autopilots, Car parks and navigation systems – software and hardware, without which driving will soon be difficult to imagine. In addition, these systems already have a security and protection function (for example, a call of special services in the event of a serious accident), and in the future this functionality will only increase.
Its use is found in cars and typical for IoT (Internet Things) solutions: for example, GM works with IBM to apply Watson to smart cars.
It is impossible not to mention the main problem of software for cars – it should take into account the features of iron, which can be used even for more than ten years, and therefore, there must be advanced possibilities for updates. And even better – software that is ahead of time.You can read more about smart car software in Compress.
About Tesla written so much and in detail that it’s even boring to tell. But not to mention this project is simply impossible. First of all, because of the unique autonomy for the production car: a set of sensors protects the car from collisions, and a 360-degree camera recognizes road markings, intersections, other cars and vehicles, pedestrians. Thus, the car independently adjusts the controls and the speed of movement. In the process of using the car, the autopilot self-learns and at the same time transfers data to the servers of Tesla Motors, whose employees analyze and improve the system.
The electronic filling of the Tesla Model S is based on the information-control system on two Tegra3 processors, the first of which is responsible for devices and sensors, and the second for entertainment and driver information via a 17-inch display. The software is based on the Linux kernel and a special shell developed by Tesla Motors. Software updates are released quite often and are downloaded “by air”.
Tesla Model X
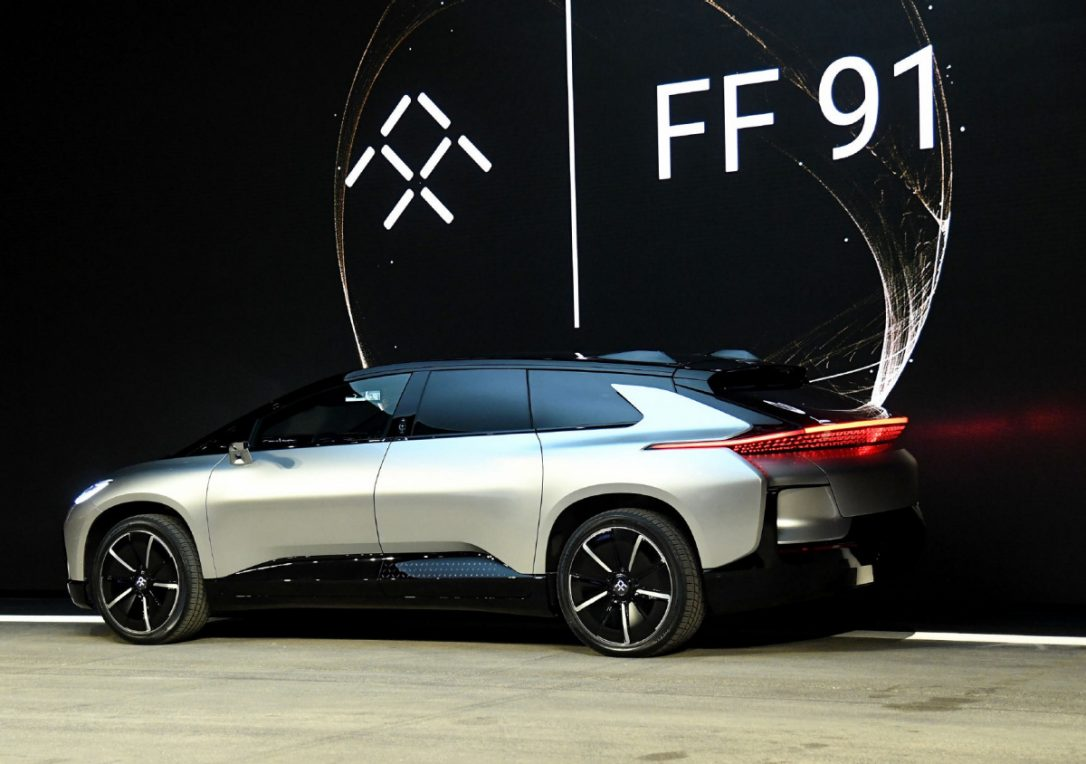
Faraday Future is a California start-up, funded by the Chinese company LeEco, which is trying to create its own ecosystem and produce literally everything . Already from the title of the project it is clear that it is an intellectual electric car and from it it is obvious that the founders of startup consider the main competitor Tesla. After a series of rumors of bankruptcy and the failure of the project, the company presented a fully-produced all-electric crossover Faraday Future FF 91 in a rather unusual streamlined body design. The car turned out overall (5250 mm in length, 3200 mm wheelbase) and ergonomic, with a low (0.25) coefficient of drag. The native Variable Platform Architecture (VPA) platform includes 4 electric motors and a battery pack. Power of electric motors in aggregate – 1050 hp, acceleration to hundreds in 2.4 seconds.
Технологии Faraday также впечатляют: 10 камер кругового обзора, 13 радиолокационных датчиков, 12 ультразвуковых датчиков и один сканер 3D LIDAR (лазерная версия радара, та самая пипка на капоте). В автомобиле можно настраивать учётные записи FFID, которые «узнают» водителя в лицо и тут же настраивают опции автомобиля именно под него.
К слову, этот кроссовер — ещё мягкий вариант китайского электроавтомобиля, первый концепт имел сверх дерзкий дизайн. Дела у компании идут с переменным успехом: в ноябре 2016 LeEco заявил о нехватке средств и жесткой экономии, а буквально несколько дней назад на CES в Лас-Вегасе кроссовер был представлен публике, но не без технических сбоев. Запуск серийного производства запланирован на 2018 год — скоро увидим, чем закончится история китайского конкурента Tesla.

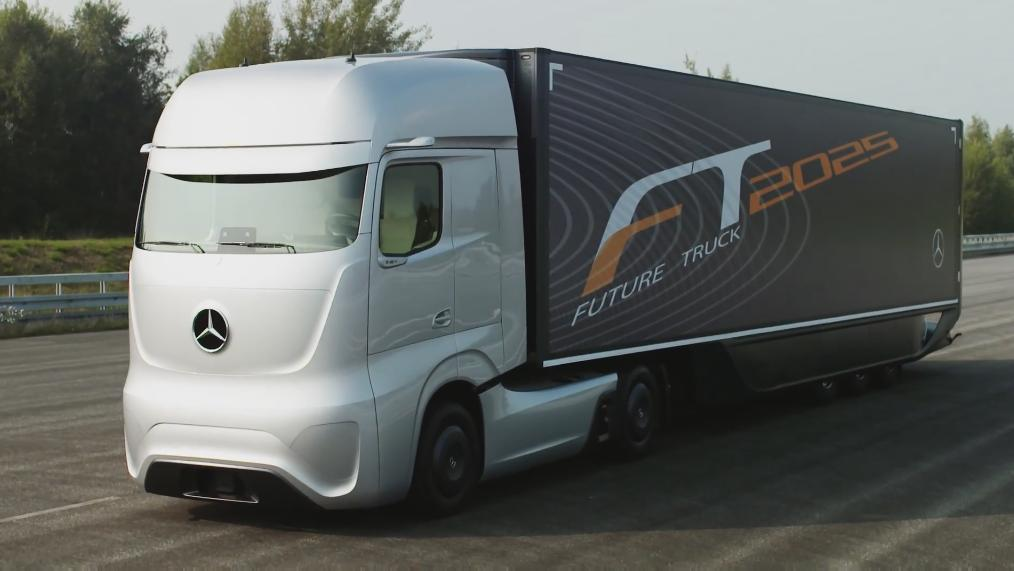
Одна из самых перспективных сфер применения платформ для беспилотных автомобилей — грузовой транспорт, который применяется в строительстве, промышленности, сельском хозяйстве. Mercedes создал беспилотник Future Truck 2025, предназначенный для передвижения по крупным трассам. Автопилотные функции реализованы на основе двойных камер, датчиков, радиолокации и технологии «мёртвой точки». Специальные радары прослушивают и просматривают дорогу, оценивая рельеф или, например, улавливая спецсигналы автомобилей экстренных служб. Во время автопилотирования водитель должен находиться внутри но может комфортно расслабиться с планшетом в руках. Для управления машиной в городских условиях такой фурой нужен водитель.

Примерно так мы и представляем дальнобойщика будущего
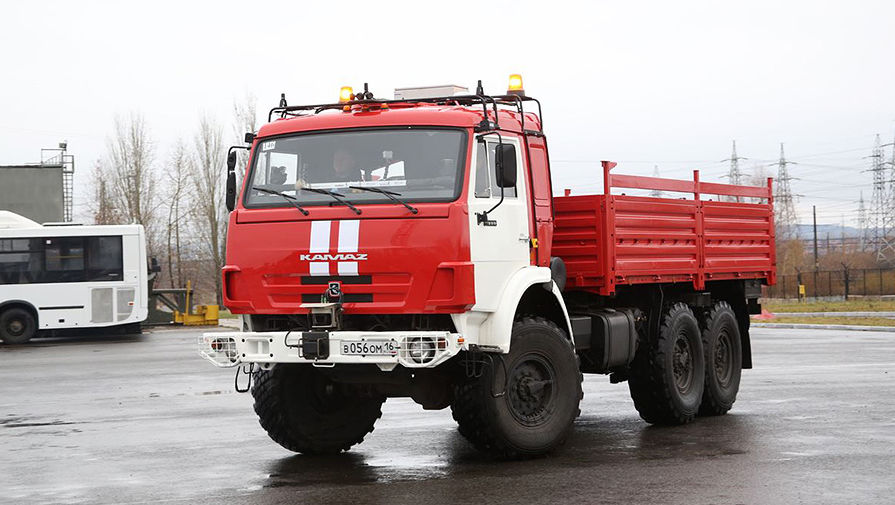
К тестам беспилотной версии приступил и российский КамАЗ. «КамАЗ» совместно с Cognitive Technologies и «ВИСТ Групп» реализует проект беспилотного автомобиля, который будет сам управлять педалями газа и тормоза, приводом руля и автоматической коробкой передач. Базой для прототипа стал серийный КамАЗ-5350, на котором установлены четыре видеокамеры, три радара и лидар — активный оптический сенсор, выполняющий роль лазерного дальномера. В кабине размещены приводы органов управления и два компьютера, соединенных локальной сетью Ethernet. Беспилотный КамАЗ использует технологию пассивного компьютерного зрения: грузовик менее, чем за 0,3 секунды обнаруживает препятствия на своём пути, распознаёт дорожные знаки и сигналы светофора. В отличие от зарубежных беспилотных автомобилей, КамАЗ проникся российской реальностью и не работает на основе распознавания дорожной разметки, нанесённой на идеально ровное шоссе.

Можно уверенно сказать, что мы живём в эру умных автомобилей, которые будут относиться к одной из трёх групп: напичканные электроникой привычные машины, беспилотные автомобили и электронные помощники. Лишний пример тому — не упомянутые выше, но присутствующие на рынке смарткаров VW iBeetle с экосистемой Apple — все бортовые электросистемы интегрированы с iPhone, и даже громоздкий и неуклюжий с виду пикап Ford F-150 с голосовым управлением. Это серийные автомобили, доступные к покупке и готовые работать на своего хозяина. В любом случае, очевидно, что развитие электронной и программной составляющей автомобилей будет развиваться, ища компромисс между потребностями в безопасности, информационной составляющей и развлечением.
Но больше всего хочется, чтобы несмотря на огромные возможности электроники осталось субъективное, но такое главное — удовольствие за рулём.









